Introduction: Unpacking the Powerhouse of Linear Motion
Hydraulic cylinders are the unsung heroes of modern industry, serving as the muscle behind everything from massive construction excavators to precise aerospace flight controls. At its core, a hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that converts fluid power into linear force and motion. While the concept seems simple, the engineering behind it is a sophisticated interplay of materials, tribology, and fluid dynamics.
Understanding the individual components is not merely an academic exercise; it is critical for ensuring system longevity, optimizing performance, and preventing costly downtime. As defined by NASA's educational resources, the operation of these components relies on Pascal's Law, which states that a pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere. This fundamental principle allows a hydraulic cylinder to multiply force, enabling heavy lifting with relative ease.
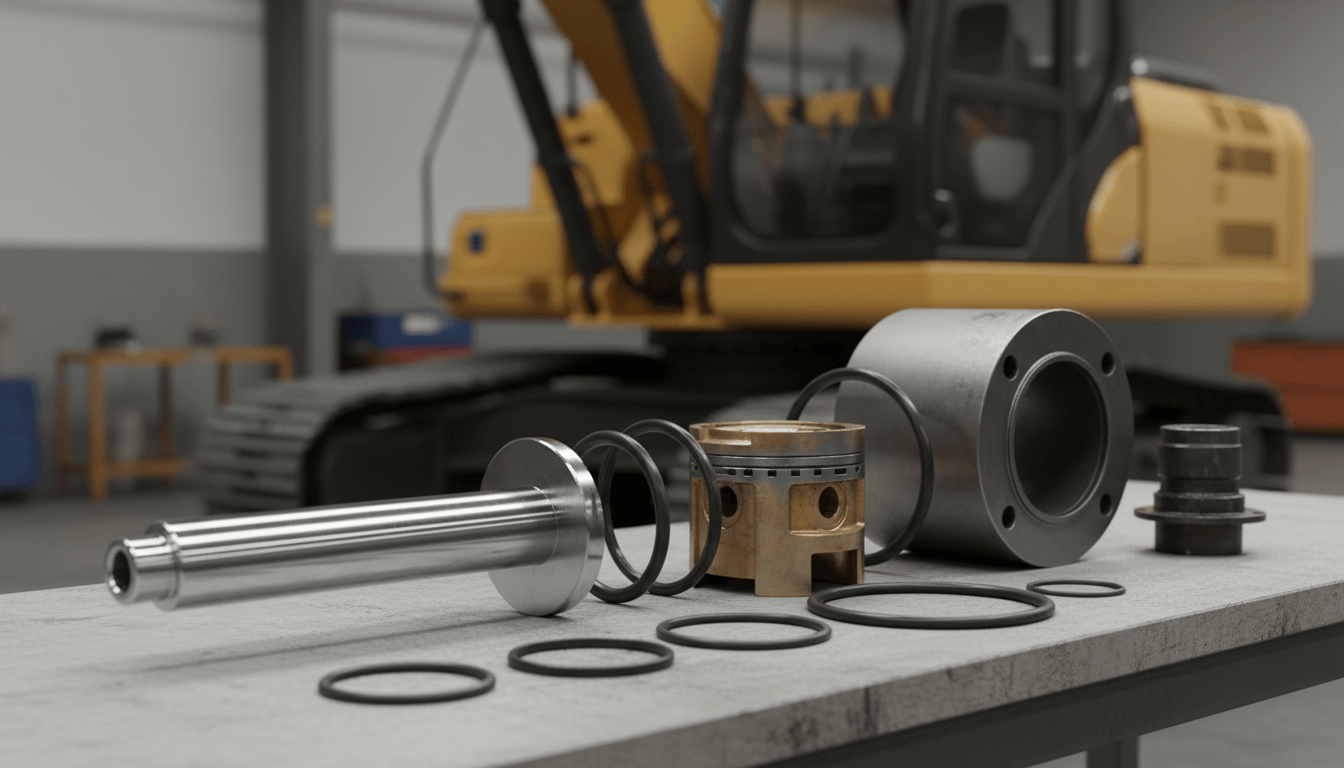
The Core Anatomy of a Hydraulic Cylinder: Essential Components Explored
To the untrained eye, a cylinder appears to be a simple metal tube. However, a look inside reveals a precision-engineered assembly designed to withstand immense pressure and friction.
Cylinder Barrel (Tube)
The barrel is the main body of the cylinder, acting as the pressure vessel that contains the hydraulic fluid.
· Function: It guides the piston and contains internal pressure.
· Materials & Manufacturing: According to industry specifications, barrels are typically made from seamless steel tubes, often honed or skived and roller burnished to achieve a surface finish of Ra 0.4 µm or better. Common materials include ST52.3 or 1045 carbon steel, while high-pressure applications may use 27SiMn alloy steel.
Piston
The piston is the internal disc that separates the cylinder into two distinct chambers: the cap end (bottom) and the rod end (head).
· Function: It serves as the sliding interface against the barrel wall, converting fluid pressure into mechanical force.
· Design: Variations include single-acting (pressure on one side) and double-acting (pressure on both sides).
· Materials: Pistons are generally machined from cast iron or steel, though aluminum is used in lighter-duty applications.
Piston Rod
The rod is the most vulnerable component, extending and retracting out of the cylinder to perform work.
· Function: Transmits the force generated by the piston to the external load.
· Materials & Finish: As noted in ISO and industry plating guides, rods are typically made from 1045 or 4140 steel. Crucially, they undergo hard chrome plating (typically 20-50 microns thick) and induction hardening to resist wear, corrosion, and scoring.
Cylinder Head (Rod End Cap) & Cap End (Base)
These components close the barrel at either end.
· Function: The Head (Gland) allows the rod to pass through while sealing the fluid; the Cap acts as the fixed base.
· Mounting: Design variations are vast, including clevis, trunnion, and flange mounts, often governed by ISO 10762 standards for interchangeability.
Seals & Glands (The Sealing System)
Often considered the most critical subsystem, seals prevent fluid bypass and external leakage.
· Rod Seals: Prevent fluid from leaking out past the rod.
· Piston Seals: Prevent fluid from bypassing the piston, ensuring efficiency.
· Wiper (Scraper): Cleans the rod as it retracts to prevent contaminants from entering.
· Materials: Selection depends heavily on fluid and temperature. Polyurethane (PU) is common for high abrasion resistance, while FKM (Viton) is used for high temperatures, and NBR (Nitrile) for standard mineral oils.
Ports
These are the fluid entry and exit points. Their design—whether SAE, NPT, or BSPP—must ensure leak-free connections under pressure, a critical factor detailed in ISO 1179 and ISO 6149 standards.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced & Supporting Hydraulic Cylinder Components
High-performance cylinders rely on more than just the core parts. Understanding the basic hydraulic cylinder components is essential before diving into these advanced elements.
Bushings & Bearings (Guide Bands)
These components support the piston and rod, preventing metal-to-metal contact between moving parts. Composite or bronze bushings handle side loads (lateral forces) that could otherwise score the barrel or bend the rod.
Cushions
To prevent shock damage at the end of a stroke, cushions trap a small amount of fluid to decelerate the piston. This hydraulic braking acts as a damper, significantly extending the cylinder's life.
Tie Rods
Specific to tie-rod cylinders (common in industrial automation), these high-strength steel rods hold the end caps against the barrel. Proper torque application is essential to maintain structural integrity under pressure.
Sensing Devices
Modern "smart" cylinders increasingly integrate linear position sensors and pressure transducers. These devices provide real-time feedback to the control system, enabling precise positioning and predictive maintenance—a trend heavily emphasized in 2025 industrial outlooks.
How Hydraulic Cylinder Components Work Together: A System Perspective
The magic happens when these components interact. In a double-acting cylinder, pressurized fluid enters the cap-end port, pushing against the piston's surface area. The seals hold this pressure, forcing the piston and rod to extend.
Simultaneously, fluid on the rod side is forced out through the rod-end port. To retract, the flow is reversed. The piston rod's volume reduces the effective area on the retraction side, meaning retraction is typically faster but produces less force than extension—a nuance defined by the differential area ratio. The cylinder relies on a hydraulic pump to maintain consistent pressure and flow, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the system.
Selecting the Right Hydraulic Cylinder Components: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right components requires a holistic assessment of the application.
1. Load & Pressure: High-load applications require induction-hardened rods and high-yield-strength barrels (e.g., 42CrMo).
2. Environment: Corrosive marine environments demand stainless steel or specialized ceramic rod coatings (e.g., Lunac) rather than standard chrome.
3. Fluid Compatibility: As highlighted by Trelleborg Sealing Solutions, using incompatible seal materials (e.g., NBR with phosphate ester fluids) leads to rapid seal swelling and failure.
4. Temperature: Extreme heat (>150°C) dictates the use of FKM or PTFE seals and specific barrel alloys.
Common Component Failures, Troubleshooting & Preventative Maintenance
Even the best components fail without care.
· Piston Rod Scoring: Often caused by abrasive particles or worn wiper seals. If the chrome plating is compromised (<20 microns remaining), seal failure is imminent.
· Seal Extrusion: High pressure can force seal material into the gap between the piston and barrel. Anti-extrusion rings (backup rings) are the solution.
· Ballooning: Excessive pressure can cause the barrel to deform permanently. This is a structural failure often linked to exceeding the hoop strength specifications.
· Diesel Effect: Air trapped in the hydraulic fluid can compress rapidly, igniting and burning seals—a phenomenon known as dieseling.
Preventative Maintenance: Regular fluid analysis to check for ISO cleanliness codes (e.g., 18/16/13) is the single most effective way to protect internal components.
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Hydraulic Cylinder Components
Top-tier manufacturing involves rigorous standards:
· Honing: The barrel bore is honed to a cross-hatch pattern to retain lubrication.
· Plating: Rods are chrome plated via electroplating, then polished.
· Testing: Finished cylinders undergo pressure testing (typically 1.5x operating pressure) to verify seal integrity and barrel strength.
· Standards: Leading manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 for quality management and specific product standards like ISO 6020 (Industrial cylinders).
The Future of Hydraulic Cylinder Components: Innovations & Trends for 2025 and Beyond
The industry is shifting towards Cyber-Physical Systems.
· Smart Hydraulics: By 2025, the integration of IoT sensors directly into cylinder heads for monitoring temperature, vibration, and cycles is becoming standard for critical assets.
· Sustainability: New low-friction seal geometries are being developed to reduce energy consumption, alongside a push for bio-based hydraulic fluids that require compatible elastomer components.
· Advanced Materials: Research into DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings offers rods that are harder and slicker than chrome, reducing friction losses significantly.
Conclusion: Mastering Hydraulic Cylinder Components for Optimal Performance
From the humble seal to the robust barrel, every component in a hydraulic cylinder plays a non-negotiable role. Mastering these elements allows engineers and maintenance professionals to design more efficient systems, troubleshoot with precision, and extend the lifecycle of their machinery. As we move into 2025, the fusion of traditional mechanical robustness with digital intelligence will define the next generation of hydraulic components.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the single most critical component of a hydraulic cylinder?
While all components are interdependent, the sealing system is often considered most critical. Seal integrity directly impacts efficiency, prevents fluid bypass, and protects against contamination. A single seal failure can render a massive machine inoperable.
How do I identify the different parts of a hydraulic cylinder without a diagram?
The barrel is the large, main outer tube. The piston rod is the shiny, chrome-plated shaft that extends out. The end caps are the blocks or round covers at each end of the tube. Ports are the threaded holes for hose connections, usually found on the end caps.
What are the most common causes of hydraulic cylinder seal failure?
The leading causes include abrasion from contaminated fluid, heat hardening from high operating temperatures, chemical incompatibility with the fluid, and extrusion caused by pressure spikes or excessive gaps between metal parts.
Can I mix and match components from different hydraulic cylinder manufacturers?
Generally, no. Even if cylinders look similar, internal tolerances, thread pitches, and seal groove dimensions often vary. Mixing parts can lead to catastrophic failure. However, ISO standard cylinders (like ISO 6020) are designed for dimensional interchangeability of the complete unit, though internal parts may still differ.
What are the key differences between a single-acting and double-acting cylinder's internal components?
A single-acting cylinder typically has seals only on the piston side that holds pressure, and often includes a spring for return. A double-acting cylinder features a piston with seals on both sides to seal pressure in both extension and retraction directions.
How does material selection impact the performance and lifespan of hydraulic cylinder components?
Material choice is paramount. For instance, a stainless steel rod is essential for corrosion resistance in marine use but is softer than chrome-plated steel. Selecting the wrong seal material (e.g., using NBR in a high-temp application) will cause the seal to melt or crack rapidly.
What are tie rods specifically used for in a hydraulic cylinder, and why are they important?
Tie rods are high-tensile steel rods running the length of the cylinder. They clamp the two end caps to the barrel. They are crucial for structural integrity in "tie-rod style" cylinders, preventing the assembly from blowing apart under pressure.
How often should hydraulic cylinder components be inspected or replaced?
There is no single rule, but a common standard is to inspect seals and rods every 2,000 to 5,000 hours of operation, or if any external leakage is spotted. In severe duty (e.g., mining), inspections should be more frequent.
References
· NASA: Pascal's Principle and Hydraulics
· Wikipedia: Pascal's Law
· Market Research Future: Hydraulic Cylinder Market Trends




















Sparkling Machinery Co.,Ltd
foreverlucia1
Whatsapp: +8613609010879